Sometimes we find new, patented technologies being used in products. at other times, combining common technologies with just a spot of thoughtful design gives rise to a different—and admired—product. Here is a small sample of recent innovations that combine both the categories. take a look at them, and imagine how the engineers would have gone about making them. Perhaps it will spark a new idea in your head!
Compact, wearable GPS tracker
‘i’m Here’ is a cute little GPS tracker that ensures you lose nothing. It is so small that it can be simply put into a bag or suitcase, or worn as a pendant, enabling you to track everything from your handbag to your cat, child or grandmom. Suppose you do not remember where you left your handbag, simply ping the ‘i’m Here’ tracker inside it to immediately get its location in response. Using the desktop or mobile version of ‘i’m Cloud,’ you can see its location on a map too. Apart from pinging the ‘i’m Here’ device, it is also possible to request the location from the ‘i’m Cloud’ panel.

You can also set up the device to get constant updates on its location. You can locate it for free the first200 times. Thereafter, you need to pay a very, very nominal price per ping. The device will be available in India from May 2013, for less than Rs 10,000.
Inside: The device is very small, measuring just 3.7×3.7×1.5 cm3. It has a built-in rechargeable Li-Po 300mAh battery, which can be charged via USB and gives a standby time of two to three days. i’m Here works using a built-in Zeromobile SIM for GSM connectivity. The GPRS module is quad-band 850/900/1800/1900 MHz, multi-slot class 10, mobile station class B and GSM phase 2/2+ compliant. It uses USDD protocol for information exchange. The GPS receiver is a 42-channel, GPS L1 C, A code, high-performance STE engine. GPS functionality is extremely fast, and the time-to-first-fix just around 30 seconds for cold starts and one second for hot starts.
Storm-warning radios
Alot of equipment work quite well but fail us in emergencies. However, nowadays the trend seems to be in favour of designing equipment for emergencies. We read about SpareOne battery-powered emergency phone in the February issue of EFY, and now here is an emergency clock radio that gives storm warnings and updates.

Eton Corporation’s ZoneGuard+ looks like a simple clock cum radio but whirrs into action when there is a storm ahead. The LED lights turn from green to orange to red depending on the intensity of the emergency, and the warning is broadcast on all the modules. While the package comes with one base station and two wireless modules, you can add any number of modules—even one for every room—to make sure you are always alert.
Inside: ZoneGuard+ features an LCD display, speakers, AM/FM radio, digital tuning, alarm clock and AC/battery power. Specifc-area message encoding (SAME) data from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, USA, is used for detecting storms. You just need to enter your SAME county code and if there is a warning, watch or advisory, it will be displayed and broadcast on all the modules. You can set up to 25 locations. Wireless modules, which are powered by a pair of AAA-size batteries, work within a range of 50 metres around the base station.
World’s first 3D direct ear scanner
Lantos 3D digital ear scanner is apparently the world’s first inra-aural 3D scanning system. The small handheld device produces a 3D image of the patient’s ear canal. Rather than providing a fxed image, it shows the changes that take place in the shape of the canal as the patient moves or swallows, and a lot of other data about the ear canal wall that manufacturers can use to improve the fit and design of in-ear devices. It can also beused by hearing device makers to understand the human ear better. Lantos’ device is likely to be available commercially sometime this year.
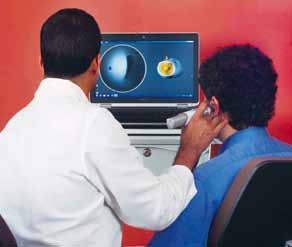
Inside: The Lantos scanner uses a fiberscopeenclosed in a conforming membrane, which is inserted into the ear canal. The conforming membrane is then filled with an asorbing medium, causing the membrane to expand and conform to the shape of the ear canal. The fiberscope then retrcts to generate a dynamic, 3D image of the ear canal in real time. The entire scan takes less than 60 seconds, after which the images are processed.
The Lantos scanner is based on a new technology called ‘emission re-absorption laser-induced fluorescence’(ERLIF), developed by Dr Douglas Hart at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Using the intensity measurement of two different wavelength bands of fluorescent light as they travel through an absorbing medium, ERLIF generates a highly-accurate 3D map. The medium selectively absorbs one wavelength band over the other. Thus the intensity ratio of the two wavelengths as they travel through the medium can be measured using a standard camera.
Turn your iPhone into a bike trainer
Wahoo Fitness’ KICKR is a super trainer for cyclists. Using an application running on your iPhone and the wireless-enabled power trainer device, you can stay indoors and practice as if you were on the ground. The KICKR power trainer allows cyclists and triathletes to set the resistance and ride the bike while accurately measuring power, heart rate, speed and other parameters. Users can increase or decrease the resistance and simulate real-world conditions. They can also structure interval workouts. These adjustments occur almost instantaneously, so the user can go from gradients to flatland, and then steep slopes again, almost immediately. An application called Kinomap also lets you choose from various cycling tracks and eco-locations, to simulate the environment automatically.

Inside: KICKR power trainer uses a wheel-off design and super fly-wheel that produce a realistic road feel and work very silently. It measures power at the hub, giving consistent and accurate readings. The trainer includes an internal thermocouple to self-calibrate the strain gauge based on temperature variations. The resistance is driven by your iPhone or tablet during the ride and you can go from a 15 per cent gradient to a downhill run immediately. There are ten built-in resistance levels as well as a full manual mode that lets you stay in control.
The device can dual-broadcast the power and speed on ANT+ and Bluetooth Smart/Bluetooth 4.0 simultaneously. This means it is compatible with almost all current ANT+ power meter head units like the Garmin FR310XT/FR910XT/Edge 500/Edge 705/Edge 800, CycleOps Joule units, Timex global trainer and Magellan switch. What is more, the power trainer works on a completely free and open platform. So anyone with programming skills can create an application for it.
Neck-loop, audio-streamer for hearing-aid users
ClearSounds’ Quattro XS is an amplifie, Bluetooth neck-loop with advanced audio distribution profile (2DP). Perfect for hearing-aid users, it ensures that they hear perfectly in any environment. Transmission of sound from a Bluetooth-enabled mobile phone, directly through the T-coil of a hearing aid, reduces or eliminates interference between cellular phones and hearing aids or cochlear processors. It also tries to shut off background noise to a large extent. The device provides voice-controls for volume, amplification, dialling, etc.

Inside: Quattro XS features a binaural design. It includes an amplifierand removable Bluetooth microphone, as well as a user-friendly noise-cancelling neck-loop. A push-button slider is used to cinch the neck-loop for closer microphone placement. The device uses a universal micro-USB for fast charging and includes an attachable Bluetooth mini-microphone transmitter, intercom features, talking caller ID, and sophisticated profilesignal handling between the Bluetooth device and neck-loop signal interface. The headset jack accommodates audio headsets for non-T-coil use. Quattro offers 30dB adjustable amplification,and supports various profilesincluding hands-free, headset, A2DP and audio/video remote control profile.It is compatible with standard Bluetooth Version 2.1 + EDR devices, and has a range of 9 metres (30 feet). It uses a Lithium-Ion battery that offers a talk time of up to three hours and standby time of five days. It can be charged through USB cable,car adaptor or AC adaptor, all of which are included in the package.
Control battery-powered devices wirelessly
Power management solutions are all the rage. We keep hearing about controllers for air-conditioners, lighting systems, computers and so on. But what about smaller, battery-powered devices? Is it possible to turn off your radio through your mobile phone? Yes, Tethercell, an innovative product developed by Trey Madhyastha and Kellan O’Connor, veterans of the aerospace industry, lets you control the gadget you want. Just remove one of the AA-size batteries from the gadget and replace it with a Tethercell adaptor, which is a little app-enabled device with the dimensions of an AA-size battery. You can now remotely control the gadget through an app running on your iOS or Android device. Tethercell will be available commercially from June 2013.

Inside: Tethercell contains a lot of cutting-edge electronics based upon the TI CC2540 microcontroller. It also contains a current-sensing op-amp comparator, temperature sensor, n-channel MOSFET (capable of switching up to 5A), 1.5-3V boost converter and embedded 8051 microcontroller. The device is powered by a single AAA-size battery. Powering the on-board Bluetooth radio consumes just around 20 mA of current. However, the radio operates on a low-duty cycle, and spends most of its time in ‘sleep mode.’ In cases where Tethercell is used merely for switching on or off devices, it will be able to run for approximately six to twelve months on a single AAA-size battery. However, when it is configure to do more tasks and the host device draws more power, the battery might need replacement earlier. Tethercell utilises Bluetooth 4.0—the new low-power Bluetooth protocol that is expected to play a huge role in the Internet of Things. It has a range of around 18 metres (60 feet) indoors and 30 metres (100 feet) in open grounds.
Users will be able to tailor the behaviour of their Tethercells using the Tetherboard app with simple iOS-style app controls. An app developer kit can also be downloaded for free to build your own applications. The device also takes care of your privacy by including password protection.


















 Imagine that you’ve decided to organize your closet, but instead of measuring containers at a store to make sure they will work, you just go to your office, enter the measurements you want your containers to be, and print them out right there. Now imagine that you have to build a diorama of a famous Civil War battle for a project at school, and you use that same printer to construct all the soldiers, cannons and trees in perfect detail.
Imagine that you’ve decided to organize your closet, but instead of measuring containers at a store to make sure they will work, you just go to your office, enter the measurements you want your containers to be, and print them out right there. Now imagine that you have to build a diorama of a famous Civil War battle for a project at school, and you use that same printer to construct all the soldiers, cannons and trees in perfect detail.